Capsaicin is a chemical component of chili peppers that give them their spicy heat. Though widely popular for spicy food lovers, it also offers certain health benefits and pain relief. Learn more about capsaicin below.

Scoville Heat Units: 16 Million
What is Capsaicin?
Capsaicin is essentially the ingredient that makes chili peppers hot. When you bite into any kind of hot pepper and you get that spicy kick on the tongue, love it or hate it, it's the result of capsaicin.
It is considered an irritant to humans and other mammals, producing a burning sensation when it touches mucus membranes, which is the reason why so many people love to consume it.
It's also the reason why you should be very careful with your hands after you are done handing any sort of hot pepper - most people have made the mistake of rubbing their eyes or some other sensitive area of the skin after touching a hot pepper at least once, but usually you won't do it again!
Capsaicin is one of a collection of similar compounds called "capsaicinoids" that give chili peppers their pungent heat. It is thought to have evolved in peppers as a defense against fungi and possibly mammals.
What are Capsaicinoids?
Capsaicinoids are the chemical components in capsicums that give them their spicy heat. The most common and most abundant capsaicinoid in chili peppers is capsaicin. Here is a list of them in descending order of pungency.
- Capsaicin - 16 Million SHU
- dihydrocapsaicin - 16 Million SHU
- nordihydrocapsaicin - 9.1 Million SHU
- homocapsaicin - 8.6 Million SHU
- homodihydrocapsaicin - 8.6 Million SHU
These 5 chemicals occur naturally, but one has been synthetically created, called "vanillylamide of n-nonanoic acid" (VNA, or PAVA).
How Hot is Capsaicin?
Pure capsaicin measures in at 16 Million Scoville Heat Units on the Scoville Scale. The Scoville Scale and Scoville Heat Unit (SHU) were named for scientist Wilbur Scoville in 1912.
It is a test used to measure a chili pepper's pungency and heat. A typical jalapeno pepper, for example, has only a bit of capsaicin within it, as it averages 5,000 Scoville Heat Units.
Pure capsaicin, therefore, is about 3200 times hotter than a jalapeno. That is very hot.
Learn more about the Scoville Scale here, or my post on What Makes Chili Peppers Hot.
What is the Chemical Makeup of Capsaicin?
The chemical formula for capsaicin is C18H27NO3. Here is the graphic representation.
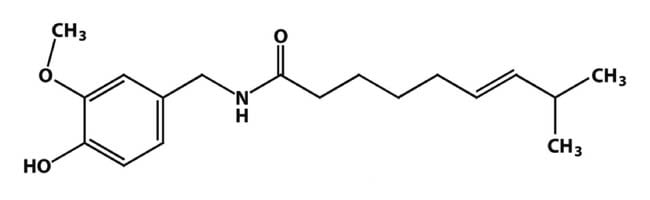
How to Stop the Burn in Your Mouth or On Your Skin
Most of the heat from chili peppers comes from the pithy whitish pepper innards, so removing or coring that material from the peppers before cooking will help to reduce the heat.
However, if you feel the burning sensation on your skin or in your mouth from peppers, your best bet is to use a dairy product to combat the heat. Dairy products contain a chemical called casein that combats the effects of capsaicin by stripping it from its receptor site on the skin.
There are other ways to help. See my page for How to Stop the Chili Pepper Burn for additional methods and tips.
When handling a large quantity of hot peppers for a long period of time, it's a good idea to wear gloves to avoid the burn in the first place.
Health Benefits of Capsaicin
Capsaicin has been studied for a number of potential health benefits because of its unique chemical properties. Here are some of the top health benefits of capsaicin:
- Pain Reliever
- Weight Loss Management
- Treating Skin Conditions
- Diabetes Management
- Cancer Treatment
- Headache Relief
- Reduce Blood Pressure
Pain Reliever
As a pain reliever, capsaicin has been widely researched for its ability to activate a specific pain receptor, which causes the brain to release a pain alleviating neurotransmitter.
It has been worked into capsaicin patches, capsaicin creams and topical ointments to battle many types of pain, such as that related to rheumatoid arthritis and fibromyalgia, as well as joint pain.
One popular pain relief cream is called Capzasin, which you can purchase at Amazon (affiliate links, my friends).
Capsaicin for Weight Loss
Spicy chili peppers may speed up your metabolism, help you burn fat, and suppress your appetite. By incorporating chili peppers, and therefore capsaicin into your diet, you may able to better control your weight.
Skin Conditions
Capsaicin is known to treat a variety of skin conditions, including psoriasis and postherpetic neuralgia. The use of capsaicin creams has shown to reduce skin breakouts.
Diabetes Management
A regular diet of chili peppers has shown a positive improvement of blood sugar and insulin reactions.
Also, it is possible to treat painful diabetic neuropathy with capsaicin cream. Side effects of capsaicin skin creams include a mild burning sensation, but the trade off is worth it.
Cancer Treatment
Promises for cancer treatment has spurred a great deal of research in capsaicin. According to the research, capsaicin induced approximately 80 percent of prostate cancer cells growing in mice to follow the molecular pathways leading to apoptosis.
Prostate cancer tumors treated with capsaicin were about one-fifth the size of tumors in non-treated mice.
Capsaicin is being researched for many different types of cancers, for its ability to shrink tumors, prevent metastasis, causing apoptosis, as well as cancer prevention.
Research and clinical trials are continuous and ongoing.
Headache Relief
Studies show that chili peppers can relieve pain from migraine and sinus headaches. Capsaicin is known to inhibit a key neuropeptide, Substance P, that is the key brain pain transmitter.
Lowering Blood Pressure
Eating chili peppers are naturally high in vitamins A and C, and also bioflavinoids. They help strengthen our blood vessels, which makes them more elastic and better able to adjust to blood pressure fluctuations.
Capsaicin also can make us sweat, which causes fluid loss, temporarily reducing overall blood volume.
See more about the Health Benefits of Chili Peppers.
What is Hotter than Capsaicin?
While pure capsaicin is extremely hot, measuring in at 16 Million Scoville Heat Units, there is a resin from a Moroccan cactus-like plant that is 1,000 times hotter.
The resin spurge Euphorbia resinifera contains a chemical called resiniferatoxin, or RTX, which measures in at 16 Billion Scoville Heat Units.
That is extremely, extremely hot.
Here are some frequently asked questions about capsaicin.
Can Capsaicin Kill You?
While consuming spicy food cannot kill you unless you eat a vast amount in one sitting, pure capsaicin is classified as a poison. It registers as heat with our taste buds and triggers an inflammatory response.
In a study published in Drug and Chemical Toxicology determined an average-sized person would need to consume nearly half a gallon of Tabasco® Sauce to overdose and lose consciousness.
A fatal dose of capsaicin for a 150 pound person was determined to be about 13 grams.
Where Can I Buy Pure Capsaicin?
If you're looking to purchase capsaicin, it is best to search for "chili pepper extract". You'll find a number of hot sauces made with pepper extract, which can be extremely hot.
You'll also find various extracts with different levels of heat. Find Chili Pepper Extract Here. It's an affiliate link to Amazon, my friends.
Good luck!
Here are some links to further interest.
A List of Chili Peppers and Their Heat for Comparison
- Poblano Peppers (up to 2,000 SHU)
- Jalapeno Peppers (8,000 SHU)
- Serrano Peppers (up to 23,000 SHU)
- Cayenne Peppers (up to 50,000 SHU)
- Habanero Peppers (up to 350,000 SHU)
- Ghost Peppers (up to 1 Million SHU)
- Carolina Reaper (up to 2.2 Million SHU)


DENNIS MAY says
Where can I get capsicum extract with reduced pungency.
They use it in capsol-t but I can’t find it by itself.
Thanks
Dennis
Michael Hultquist - Chili Pepper Madness says
I'd love to hear other readers' responses to this. But, you might ask your doctor.